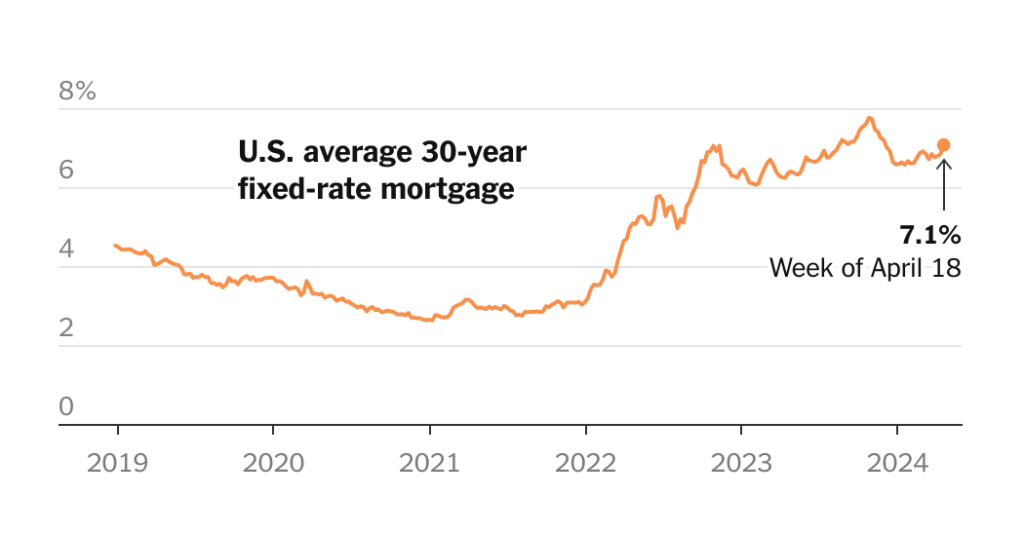Mortgage rates have risen above 7 percent for the first time this year, reaching 7.1 percent, the highest since November. This increase has caused concern for potential home buyers and sellers, who may be deterred from entering the housing market. Sellers who are locked into lower rates on their existing loans are keeping their houses off the market, leading to higher prices. This trend, along with rising mortgage rates, has contributed to frustration about the economy, particularly as inflation remains higher than expected.
With mortgage rates on the rise, potential home buyers are facing a dilemma of whether to purchase now before rates increase further, or wait in hopes of a decrease later in the year. The increasing rates have already had an impact on the housing market, with sales of existing homes falling by 4.3 percent in March and 3.7 percent from a year earlier. This slowdown in sales is part of a broader trend of cooling in the housing market, which was previously fueled by historically low rates seen in 2021.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to raise its benchmark rate in an effort to combat inflation has contributed to the rise in mortgage rates. Despite inflation cooling significantly, the Fed has indicated that it may keep borrowing costs high for longer. The Fed’s benchmark interest rate is currently at its highest level in 22 years, reflecting its commitment to controlling inflation. Mortgage lenders closely monitor the 10-year Treasury bond, which influences mortgage rates, and the expectation of continued high rates has led to an increase in Treasury yields.
The decision by the National Association of Realtors (N.A.R.) to settle litigation that would eliminate the standard sales commission could potentially impact home prices. Currently, sellers pay a 5 or 6 percent commission to a real estate agent, which is typically passed on to the buyer through a higher sticker price. Removing this commission could result in more competitive pricing in the housing market, making homeownership more accessible to a wider range of buyers. This move by the N.A.R. reflects a broader shift in the real estate industry towards more transparent and affordable pricing for consumers.
Overall, the housing market is facing challenges due to the combination of rising mortgage rates, inflation, and potential policy changes. Home buyers and sellers are navigating a changing landscape, with uncertainty about the future direction of rates and prices. The impact of these factors on the broader economy is uncertain, as the housing market plays a significant role in driving consumer spending and economic growth. As the market continues to evolve, stakeholders will need to adapt to ensure a stable and sustainable housing market for the future.