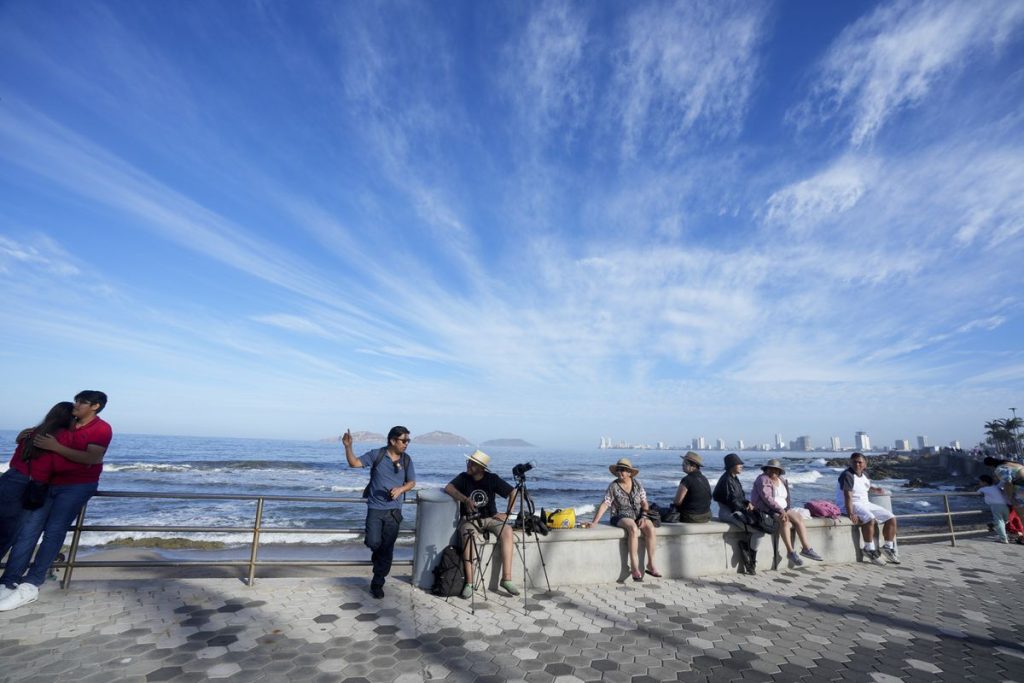
The live narration of the solar eclipse is about to begin as the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, causing a total solar eclipse in several cities in Mexico. The eclipse is expected to occur around 11:00 am local time (shortly after 8:00 pm in the Iberian Peninsula), with the Moon’s shadow completely blocking the sunlight and creating darkness that may last up to four and a half minutes. Unfortunately, the eclipse will not be visible in Spain, and can only be observed within a 200-kilometer-wide strip that will start in the Pacific Ocean, cross through the central United States, and end in the Atlantic Ocean after passing through the eastern part of Canada.
This rare phenomenon of a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly in front of the Sun, blocking its light from reaching the Earth. During a total solar eclipse, the sky darkens as the Moon casts its shadow on the Earth, creating an otherworldly experience for those fortunate enough to witness it. This celestial event is a reminder of the vastness and beauty of our universe, as well as the intricate dance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth that results in such captivating displays.
In Mexico, where the eclipse will be total in certain areas, spectators are preparing to witness this natural spectacle, with special glasses and equipment to safely observe the event without damaging their eyes. Cities along the path of the eclipse are hosting viewing events and celebrations, inviting people to come together and marvel at the wonders of the cosmos. Scientists and astronomers are also taking advantage of this opportunity to study the Sun and its corona, gathering valuable data that can help us better understand our closest star.
The eclipse’s path, crossing over Mexico, the United States, and Canada, offers a unique opportunity for people in different regions to come together in shared awe and wonder, united by their observation of this rare event. Through social media and live broadcasts, people around the world can join in the experience, witnessing the eclipse from different perspectives and sharing in the excitement of this celestial occurrence. This unity in diversity, as people from various backgrounds and locations come together to witness the eclipse, highlights the universal fascination and curiosity that the cosmos inspires in humanity.
As the eclipse progresses, slowly darkening the sky and dimming the sunlight, people are reminded of the fragile and interconnected nature of our existence on Earth. The beauty and majesty of the solar eclipse serve as a humbling reminder of our place in the universe, encouraging reflection on our impact on the planet and our responsibility to protect and preserve it for future generations. By coming together to witness and appreciate the wonders of the cosmos, we are reminded of the importance of unity, curiosity, and appreciation for the natural world that surrounds us.